Description of key terms
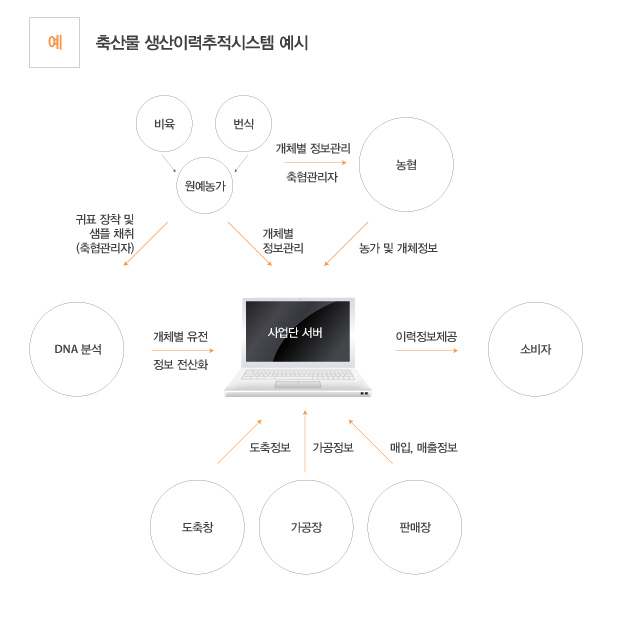
Production history tracking system
It is a system that tracks all processes from seeding and breeding of agriculture, fish, shrimp and forest products to processing, distribution (including transportation and storage) and sale.
The system records main stages to tract Farm to Table reversely by consumers and searches its contents via NS code, RF-ID, naked eyes, mobile phone and internet.
It is also called ‘production history information tracking system’ or ‘production distribution history information system’.
HS Code
It is an abbreviation of the harmonized commodity description and coding system applied from 1988 onwards. It is internationally same giving serial number to each product.
The importing country decides what code to assign to a particular product, and the tariff rate differs according to this code number. Therefore, it is advantageous for the exporting country to receive a code with low tariffs, and the importing country to receive a code with a high tariff rate.
Meanwhile, domestic DMB mobile phones have been classified as TV receivers in Germany, and 14% of TV receivers’ tariff has been applied, resulting in a dispute between the two countries. This is because the tariff rate of mobile phones is 0%. On August 7, 2009, the Customs Regulatory Commission (under the EU Executive Committee) announced in the EU Gazette that the DMB mobile phone was classified as a regular mobile phone and thus determined to be duty-free. As a result, Germany has already paid back 15 billion won in tariffs to Korea.
HACCP and SSOP correspond to computer software, and GMP or hygiene program corresponds to hardware.
Even if the S/W is excellent, if the H/W is insufficient, it is difficult to operate, and if the H/W is not good, if the S/W is not available, HACCP introduction shall be based on proper manufacturing environment conditions.
1960s: Pillsbury organized the idea for food manufacturing in the US space plan
1971: First outline announced at the National Conference of Food Protection
1973: The regulation of low acid canned foods introduced by the FDA
1985: The NAS’s Food Protection Committee evaluates the effectiveness of this approach and recommends the introduction of HACCP, which enforces voluntary hygiene and quality control in this way for food producers, and legal enforcement for administrative authorities, respectively
1988: ICMSF recommended WHO to introduce HACCP to international standards
1989: NACMCF submitted HACCP guidelines, among which the 7 principles of HACCP are first proposed
1992: NACMCF submitted revised HACCP guidelines
1993: Guideline of HACCP implementation suggested by the FAO/ WHO Codex
1995: Application of HACCP regulation as a mandatory provision for marine products Dec/ Establishment of HACCP regulation in Korea’s Food Sanitation Act (Article 32-2)
1996: USDA’s FSIS7 applied HACCP to prevent food and poultry hazards December 5 / HACCP confirmation notice (Ministry of Health and Welfare Notice No. 1996-75)
2001: Applied to the front of the food / Excluded the forced application, induced self-application
PL Code
A law enacted to protect victims from damage caused by defects in their products.
It is a law that makes the obligation of indemnifying the person who manufactured or processed the goods to the life or the body damage caused by the defect of the goods or property damage.
This is to protect the victims, raise the awareness of the stability of the people’s lives and the safety of the products and improve the competitiveness of enterprises.
It describes defects in manufacture, design, display, definition of terms such as manufacturer, liability and solidarity responsibility for products, reasons for exemption and statute of limitations. The main contents are as follows:
The term manufactured goods used in the law means any manufactured or processed personal property including any other movable property or a part of real property. Any person who has to compensate for life, body or property damage caused by defects in the manufacture, design or indication of a product is a person who manufactures, processes, or imports the product, or who signs himself or herself as a manufacturer or mistake it as a manufacturer. If the manufacturer is not known, the supplier is also liable for damages.
In the event that the manufacturer fails to supply the product or the presence of a defect at the level of science or technology at the time of the supply of the product, the deficiency of the product is the result of complying with the standards established by the laws and regulations at the time the manufacturer supplied the product. In the case of proving such fact, the liability for damages can be avoided. If there are two or more persons who are liable to compensate for the same damages, they shall be jointly and severally liable.
Any special agreement that excludes or restricts the manufacturer’s liability under the Product Liability Act shall be null and void and the limitation of the claim shall be limited to three years from the date of the loss and the manufacturer. It consists of Article 8 and Appendix.
The legislation of product liability laws in each country is as follows.
In the United States, it was established by precedent since 1960, and the United Kingdom enacted it in May 1987 and implemented in March 1988. Germany enacted it in December 1989 and enforced in January 1990, and China enacted it in February 1993 and implemented in September 1993. Japan enacted it in June 1994 and enforced in July 1995, and Korea enacted it in July 2002 and implemented two years and six months after enactment of the law in January 2000.
The PL method is the greatest assumption that a defect in the product caused physical or property damage. As I have mentioned in the example, if it hurt hand due to the sharpness of the PCB by inserting the graphics card, it can see it as the damage of the body. If it tries to smoke with the lighter and suddenly burn the tie due to excessive fire,
As seen in the above example, the most basic premise of PL law is that it has to suffer damage to body or property. Let’s say that I entered the graphics card and was hurt by the sharpness of the corner of the PCB, and the company was judged based on the P.L. First of all, because of the sharpness of the edge of the PCB, the writer (consumer) is scarred, which is contrary to the PL method and is truly a design flaw. In designing, consumers should not be harmed because they suffered from design flaws. First, what is a defect? The combination we often think of is the product’s fault.
In other words, if the vendor fails to show the characteristics of the specified product, it uses the word defect. If a person buys an MP3 player that supports USB and the USB port is not compatible with computer, it often says it is defective. However, defects in the PL method have other meanings and have a broader meaning. First, considering the characteristics of the product, the type of usage expected, and the timing of delivering the product, it is considered defective if the consumer does not provide the expected safety. If a user drills a wall and cracks on the wall during curing, it is considered to be a defect because it does not consider the stability of the user in making the drill. These defects are largely divided into three categories, namely, design defects, manufacturing defects, and defects due to lack of warning indication.
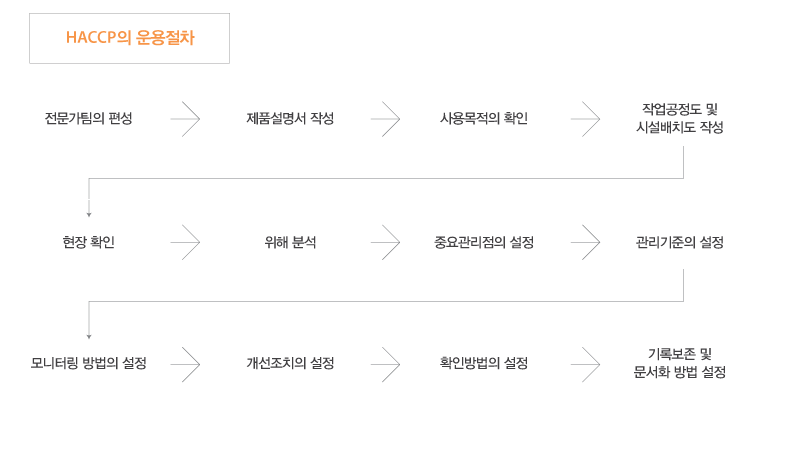
HACCP
HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point. It is a synthetic word of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point. As in the term, HACCP is about analyzing the safety hazards of the food, and how and where to manage the hazards.
In other words, it is a HACCP to derive the method from a successful case that secures the safety of the food by the process control in advance of the post – action method of inspecting the final product.
The key to HACCP is ‘preventative’.
The HACCP system refers to the planning and implementation of a holistic system that can more efficiently manage food hygiene, rather than specific standards or standards required for hygiene control of the product. When the existing food hygiene inspection method is considered to focus on the safety inspection of the final product, the HACCP system is a preventive management system necessary to guarantee the production and distribution of safer products. The emphasis is on prevention.
HACCP identifies the risk factors that may occur at each stage from raw material production through manufacturing, processing, preservation, and distribution stages until the final consumer consume them, and determines important management points to focus on management It is a scientific sanitation management system to ensure food safety through effective and efficient management.
GAP
Good Agricultural Practices
The production of agricultural products, post-harvest management (including storing, washing, drying, sorting, cutting, preparing and packing of agricultural products) and cultivation at each stage of distribution Field) and the risk factors of agricultural products in order to ensure the safety of agricultural products and to preserve the agricultural environment.
ISO
ISO refers to the International Organization for Standardization, which promotes international trade in goods and services and promotes international standardization and related activities for cooperation in the fields of intellectual, academic, technical and economic activities.
In this regard, ISO publishes international standardization and related publications that promote international harmonization and adoption of international standards and related activities.
It also arranges for information exchange with ISO member organizations, as well as various activities to promote international cooperation in the field of culture and technology and cooperation with relevant international organizations.
It mainly aims to coordinate and unify the industrial standards of each country, induce international exchange of goods and services, and promote cooperation in scientific, intellectual and economic activities. (Source: International Trade Association)
The areas covered are all parts of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), except electrical and electronics, and where necessary, IEC, the World Trade Organization (WTO) and other 500 regional organizations. (Only international standards related to electrical equipment are handled by the International Electrotechnical Commission, and other standards are established by the International Organization for Standardization.)
1906: International Electrical Conference (London, 13 countries)
Preparation of the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
1908: October International Conference (London), IEC Foundation
1926: Established SA (Int’l Federation of National Standardization Association)
1942: World War II outbreak – withdrawal from all ISA member countries, suspension, and transfer to UNSCC
1946. 10: UNSCC London Conference (25 countries participated) Decision of establishment of ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
1947. 02: ISO launched (2.23)
1951: Initial ISO standard publication (Standard reference temperature for industrial length measurement)
Bar Code
It is a printed bar of lines with different width for the purpose of entering data into a computer system.
The bars are usually black on a white background, and the width and number of the bars are different from case to case.
Bars represent binary digits 0 and 1, and arrays of bars represent decimal numbers 0 through 9, which can be processed by a digital computer.
In the arrangement of the bars, the computer reads the presence or absence of a bar having a specific width at a specific position and interprets it as 0 or 1. Most bar code codes use two thick or thin bars, but there are also four bars. The number represented by the barcode is printed at the bottom of the barcode. Bar code information is read using an optical (laser) scanner that is part of a computer system. Have a palm-sized scanner or bar-code pen over the bar code, or have the bar code itself pass over the scanner on the other surface. The computer then stores the data of the bar code or processes it immediately.
Bar codes used in supermarkets and other stores in the United States follow the Universal Product Code (UPC), which gives each food or product a unique designation.
In the UPC system, 5 numbers on the left are used to represent the manufacturer, and 5 on the right are used by the manufacturer to represent a particular type of product.
In general, this is all the information in the barcode. (→ index: barcode scanner)
Barcode notation was introduced in the 1970s and is now commonly used for everyday commerce. Stores use barcodes to obtain the price and other data for the item when the consumer calculates the purchased item. At the supermarket’s checkout desk, when placing a scanner on a bar code of a merchandise, the computer checks the price of the merchandise and displays the number on the cash register, which is added to the amount you pay.
The biggest advantage of barcode is that when reading a barcode with a scanner, it is not just about storing information and processing it later. And the user can process the detailed information immediately. For example, in a ski area, it can attach a bar code to skiers and read the bar code with a scanner every time people ride a ski lift, so it can see how the slope is being used.
Today, bar codes are used to track a wide range of products in all areas of production, distribution, storage, sales and service. Such products include processed foods, clothing, medicines, medical products, automotive parts, computer parts, and even books from the library.
Information disclosure method
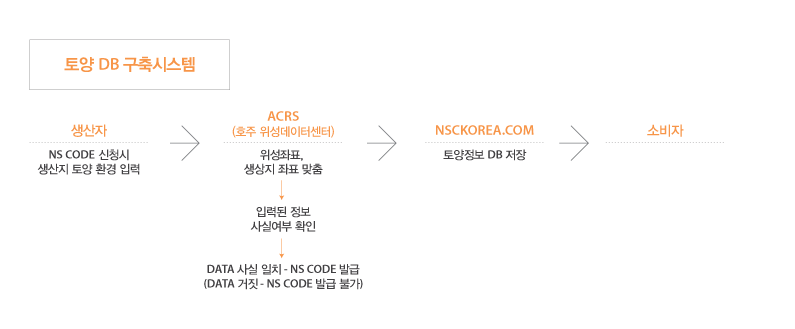
Soil – Soil for growing life
Wisdom of soil
Soil is a symbol of wisdom that gives life.
Soil is enduring quietly even in the cold weather and the breathless heat, so that soil grows softly and warmly with life, and after finally making the fruit of life. It gives out without losing any greed and makes the stars beautifully lively.
And soil quietly returns to his seat and waits to conceive the next life.
This is the image of wisdom that gives life.
Most people, however, trample, spit, dirt soils.
Furthermore, we are returning all kinds of dirty dirt and rubbish to the earth without any problem.
Soil is gradually getting wiped out.
The various information about the soil which is introduced here is that everyone is aware of the wisdom of soil by the daily consumption life with the help of the NS CODE system and cherishes the earth and treats it as a result and consequently the soil is dirty and the beautiful and rich life is sprouted These are programs designed to help to build and grow.
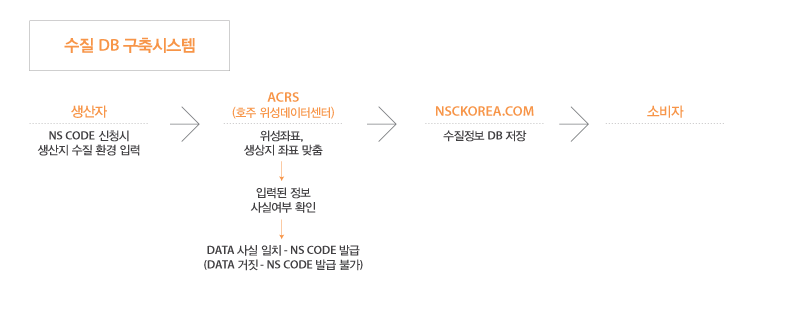
Water quality – Modestly flowing water
Modesty of water
Sangseon Spring Water which grows life at all times
From ancient times, water has been called Sangseon Spring Water.
Water always likes low places, does not struggle with others, is neither proud nor hurried.
We silently go on the way and make life around grow.
It is an object that figuratively explains the great truth that makes fruitful.
Like water and soil, people treat themselves with dirty, polluted, and destroyed water.
Now it is increasingly becoming more and more limited to explain and express the truth of this greatness.
The water introduced here is associated with the everyday consumer life together with the soil in front.
It is a program for providing information on how consumers will humbly pay for water.
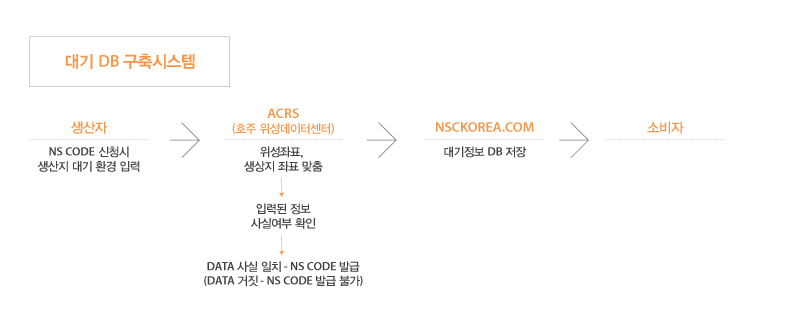
Air – Smoothly and softly blowing wind
Freedom of wind
A symbol of great freedom walking on its own way
It cannot be seen by eyes, it cannot be touched by hand, but it is the wind that can be understood through the movement of the sounds and leaves.
This mysterious wind can be a messenger of spring and a cold winter.
The wind is also something that does not hinder, quarrel or stubbornly stuck.
It is often seen as a symbol of freedom through people walking on their way.
It is the wind that is recognized. Symbol of the great freedom is the wind.
The view of the wind is too narrow
Wind started pouring various pollutants into it and it started getting worse.
NS WORLD Co., Ltd. connects the value of wind to foods everyday life of ordinary consumers.
The purpose of the NS Code system is to ensure that the consumption activity is a symbol of freedom and that the wind is running.
ISO 14000 series
ISO 14000 series
A system that minimizes the environmental impact of the production process
ISO 14000 is an international standard for the environmental management system (EMS), which is an environmentally friendly system that minimizes the impact of the production process on the environment. All processes of production, including raw material procurement and manufacturing processes, product use and product disposal can cause environmental pollution.
It is the purpose of ISO 14000 to allow companies to build self-sustaining and continuous pollution prevention systems beyond compliance with all production processes. ISO 14000 applies to all organizations and organizations as well as corporations and is subject to the principle of contributing to environmental pollution.

HACCP Criteria
HACCP
If soil, water and wind that compose our body are good, why do we need a complex hygiene management system called HACCP? The goal of the NS CODE system is to enable consumers to create food production environments that do not require HACCP.
Consumer Health Hazards Critical Control Standards
This is a hygiene management system that ensures safety by focusing on the risk factors that can cause problems including manufacturing, processing, preservation and distribution stages until the final consumer consumes food.
The core elements of HACCP are bacteria, insecticides, growth hormones, antibiotics, heavy metals, environmental hormones, radioactive materials, parasites and diseases (anthrax, foot and mouth disease, mad cow disease and tuberculosis).
HACCP is subject to the principle of polluter pays for environment pollution.


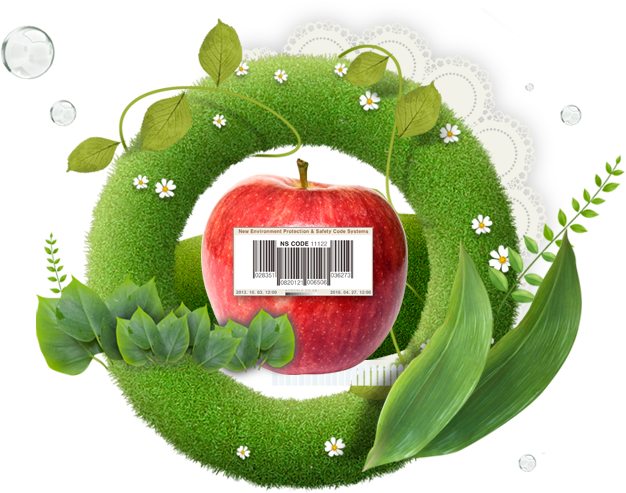
5 indicators that show information at a glance
5 Indicators of NS Code
Check food and product information at a glance.
The 5 digits shown in bold in the NS Code are called the 5 indicators, each of which consists of genetic modification, safety testing, environmental pollution prevention control, production methods and production element codes.
If the indicator closer 1, it is safer.
-> See details



